PROGERIA: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Drug Therapies
Progeria is an extremely rare genetic condition. the word ‘Progeria’comes From the Greek word pro-geras meaning prematurely old. It is also known as Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome (HGPS).It is characterized by an appearance of accelerated aging in children.While there are different forms of progeria. The classic type is Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, which was named after the doctors who first described in England in 1886 by Dr. Jonathan Hutchinson.Other progeroid syndromes include Werner syndrome, also known as ‘adult progeria which does not have an onset until the late teen years, with a lifespan into the 40’s and 50’s.
CAUSES of Progeria:
- HGPS caused by a mutation in the gene called LMNA (also known as Lamina A) in which a point mutation takes place in the LMNA gene, wherein the cytosine is replaced with thymine.
- The LMNA gene (a dominant gene) produces a lamina a protein, which holds the nucleus of a cell together.
- The abnormal Lamina a protein that causes progeria is called progerin. Progerin makes the nucleus unstable. that cellular instability leads to the process of premature aging and diseases in progeria.
- It is almost never passed on from an affected parent to child, as affected children rarely live long enough to reproduce.
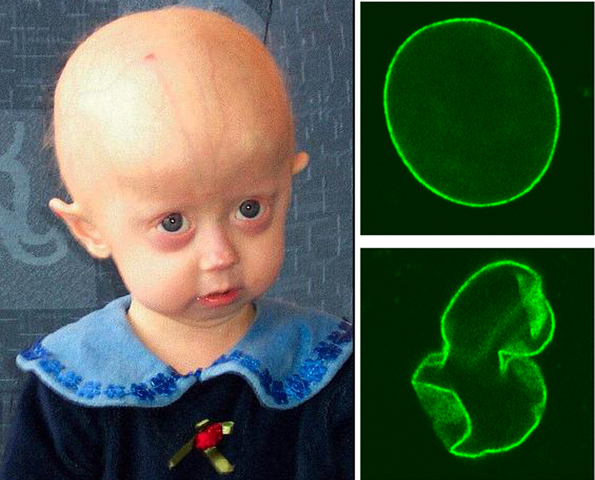
SIGNS (OR) SYMPTOMS of Progeria:
Although usually born looking healthy, most children with the progeria begin to display many characteristics of progeria within the first 2 years of life.The signs include abnormal growth, loss of body fat and hair, aged-looking skin and stiffness of joints.As they get older, they suffer from Osteoporosis, generalized atherosclerosis such as stroke, cardiovascular disease.
Skin and Hair
Skin changes at the time of birth may be present. the major abnormalities include shiny and elastic skin. the skin may appear wrinkled with low cutaneous fat. The patient is physically weak. When in contact with bright sunlight, hyperpigmentation of skin may occur with irritation. Complete loss of hair of all the body parts including scalp, eyelash, and skin.
Musculoskeletal Abnormalities
The limbs are thin with low muscular mass. The joints appear prominent. There may be flexion of knee joint leading to disturbed gait. The patient walks a bit abnormally. The thoracic cage becomes pear-shaped. The face appears like an aged person, with prominent eyes and ears slightly bigger in sizeIncisors fall at the early age.
DIAGNOSIS of Progeria:
- A genetic test for LMNA mutations can confirm the diagnosis of progeria.
- In the past, doctors had to base a diagnosis of progeria safely physical symptoms such as skin changes and a failure to gain weight, aged looking skin.
TREATMENT of Progeria:
- Although no treatment has yet proven effective, most treatment options have focused on reducing complications such as cardiovascular disease with artery bypass surgery (or) low –dose aspirin.
- Growth hormone treatment has been attempted.
- The use of Morpholinos has also been attempted in order to reduce progerin production.
- Lonafarnib is a Farnesyltransferase inhibitor (FTI, a drug that can reverse an abnormality in program cell in the laboratory, and has improved disease in progeric mice.
- Researchers have identified two additional drugs that, when used in combination with current FTI drug being tested may provide an even more effective treatment for children with progeria then FTI’s alone.
- This is pravastatin and zoledronic acid. Pravastatin is a member of the drug class of statins.
- It is usually used for lowering cholesterol and preventing cardiovascular diseases.
- Zoledronic acid is a bisphosphonate, usually used as a bone drug for improving osteoporosis, and to prevent skeletal fractures in people suffering from some forms of cancers.
- All of these drugs block the production of farnesyl molecule that is needed for progerin to create disease in progeria.
DRUG THERAPIES of Progeria:
Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy promotes relaxation, relieves pain, assists moment and enables exercise. It can also help prevent arthritis from getting worse.
Nutrin
Patients have a very small appetite and don’t really enjoy. Nutrini provides all of the nutrients essential for well-being and health.
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble vitamin that protects vitamin A and essential fatty acids from oxidation in the body cells and prevents break down of body tissues. Antioxidants such as vitamin E act to protect the cells against the effects of free radicals, which are potentially damaging by-products of the body’s metabolism. Free radicals can cause cell damage that may contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Aspirin
Aspirin is now accepted as an important weapon in the prevention of heart disease. Recent clinical trials have shown that aspirin reduces the risk of heart strokes and heart attacks. A small dose of aspirin is enough to prevent dangerous blood clotting. This is the benefit to people with narrowed coronary arteries which is commonplace in children with progeria.
Fluoride
All program children have problems with their teeth. Underdevelopment of the facial bones and the lower jaw needs to the delayed eruption of the teeth, they can be small, irregularly formed. Fluoride can greatly help dental health by strengthening the tooth enamel, making it more resistant to tooth decay.
Final word
Hutchinson-Gilford progeria of syndrome is a disease which has been a subject of curiosity among the scientists. The research is being carried out worldwide to understand the underlying cause of the disorder. Currently, FTI is being looked upon as potential drug treatment for the disease. Lonafarnib is undergoing phase II clinical trials. The drug therapies like Growth hormone, Aspirins along with various measures to prevent the complications of the disease may prove useful in prolonging the life to some extent.





